CNG vs. LNG: how to choose your natural gas fuel type
Which fuel works best for you—compressed natural gas (CNG) or liquefied natural gas (LNG)? It depends on a few things, like fuel availability in your area, the type and size of your vehicles and your required driving range.
CNG | LNG | |
|---|---|---|
What it is: | natural gas that’s been piped to a compression facility | natural gas that’s been cooled to -162 °C to become a liquid |
Best for: | medium-duty vehicles travelling a moderate distance between refuelling | the best choice when extended driving range is required because an LNG tank holds 2.5 times more fuel than a similar-sized CNG tank |
Vehicle types: |
|
|
How it’s delivered: | through our natural gas system to various dispensing stations across B.C. | From our LNG storage facilities by tank truck to:
|
Fuelling process
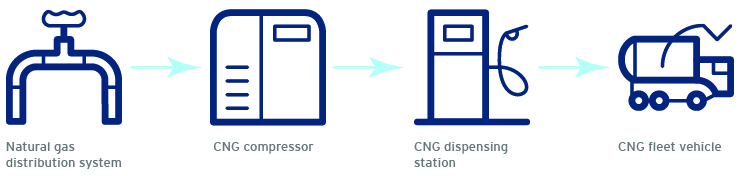
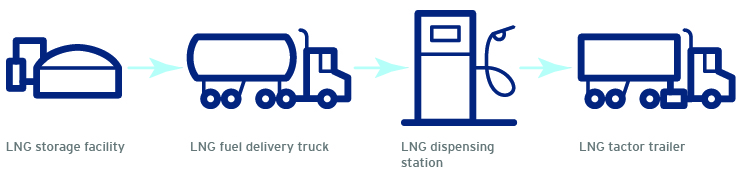
Both CNG and LNG come from our distribution system—which we continue to further decarbonize with the addition of lower carbon2 Renewable Natural Gas3 (RNG)—but there are differences on how each fuel type is delivered and dispensed.
CNG fuelling
LNG fuelling
Questions? We’re here to help.
Email us at [email protected]
1LNG delivery is an optional service that FortisBC can provide to you at a regulated rate.
2When compared to the lifecycle carbon intensity of conventional natural gas. The burner tip emission factor of FortisBC's current Renewable Natural Gas (also called RNG or biomethane) portfolio is 0.27 grams of carbon dioxide equivalent per megajoule of energy (gCO2e/MJ). FortisBC's current RNG portfolio lifecycle emissions for stationary combustion are -22 gCO2e/MJ. This is below B.C.'s lifecycle carbon intensity threshold of 30.8 gCO2e/MJ as set out in the 2024 Greenhouse Gas Reduction Regulation amendments.
3Renewable Natural Gas (also called RNG or biomethane) is produced in a different manner than conventional natural gas. It is derived from biogas, which is produced from decomposing organic waste from landfills, agricultural waste
and wastewater from treatment facilities. The biogas is captured and cleaned to create RNG. When RNG is added to North America’s natural gas system, it mixes with conventional natural gas. This means we’re unable to direct RNG to a specific
customer. But the more RNG is added to the gas system, the less conventional natural gas is needed, thereby reducing the use of fossil fuels and overall greenhouse gas emissions.